Task Manager on Mac [Activity Monitor]: A comprehensive Guide
Are you struggling to find out how to open Task Manager on Mac? Whether you're a new macOS user or looking for a refresher, understanding how to access and utilize the Task Manager, known as Activity Monitor on Mac, is essential. In this guide, we'll walk you through various methods to open and effectively use the Task Manager on your Mac. Let’s get started!
Does Mac have a task manager?
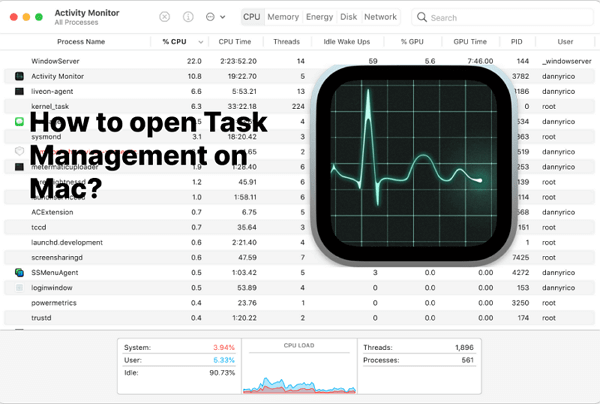
Yes, and it's called "Activity Monitor." When your Mac slows down or you encounter the spinning beach ball, having a task manager in Mac becomes crucial. This tool allows you to force quit frozen websites or applications. Windows users are familiar with the Task Manager and adept at using it to manage PC tasks for optimizing performance. Similar to Task Manager, Activity Monitor enables you to view how applications and other processes are affecting your CPU, memory, energy, disk, and network usage.
How to open Task Manager on Mac?
Task Manager, also known as Activity Monitor on macOS, is located in the /Applications/Utilities/ folder. The easiest way to open the Task Manager is by using Spotlight. Here are simple steps to follow:
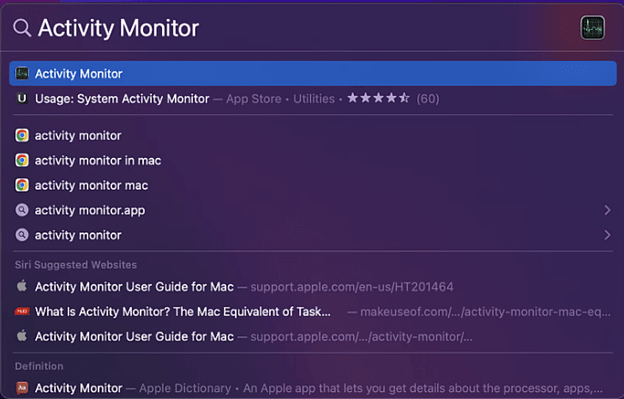
Step 1: Press Command + Spacebar to access the Spotlight search field.
Step 2: Type "Activity Monitor."
Step 3: Select "Activity Monitor" or press Enter when it appears.
Sometimes, if Spotlight fails to function properly, you can attempt an alternate method to launch "Activity Monitor." Follow the steps below:
Step 1: Click on the Finder icon in the Dock.

Step 2: From the side menu that appears, select "Applications."
Step 3: Choose "Utilities" from the "Applications" folder.
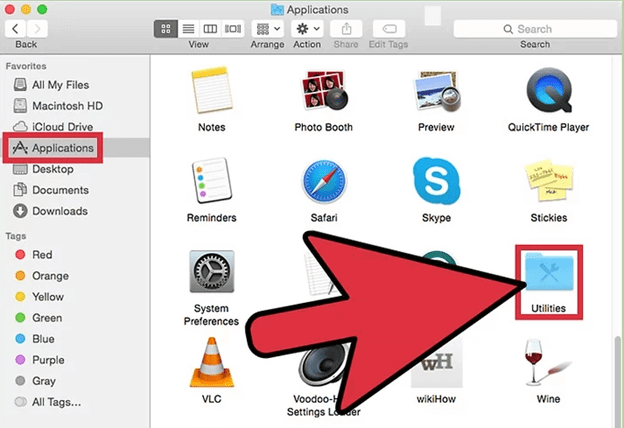
Step 4: Locate Activity Monitor and double-click to launch it.
To pin "Activity Monitor" to the Dock without the need to repeat complex steps each time you open it, you can follow these steps:
Step 1: Open Activity Monitor using one of the methods mentioned above.
Step 2: Right-click on the "Activity Monitor" icon in the Dock.
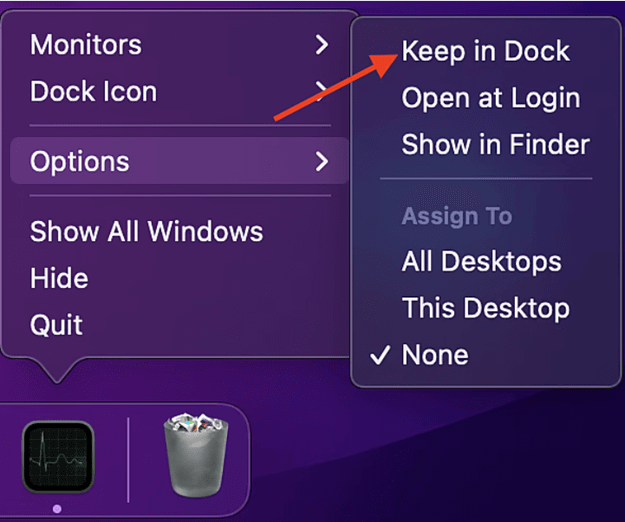
Step 3: From the menu, select "Options," then click on "Keep in Dock."
How to use Task Manager on Mac?
Task Manager offers a range of functionalities that allow users to monitor and manage system resources, troubleshoot performance issues, and optimize their Mac's performance. Here are some of the key tasks you can accomplish with Task Manager on Mac:
Troubleshooting Mac Issues with Activity Monitor

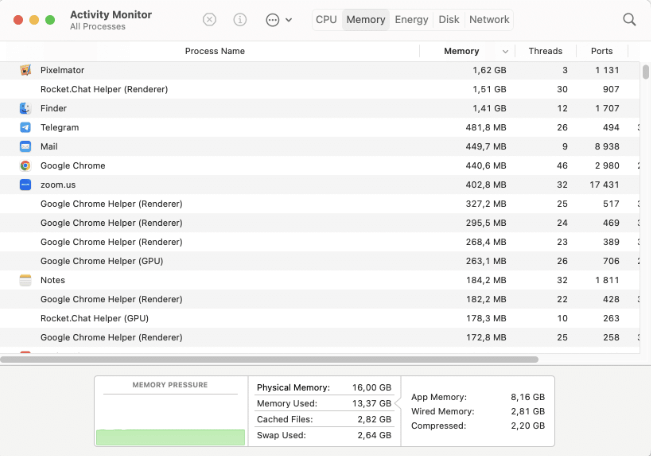
Processes displayed in Activity Monitor can be user applications, system applications used by macOS, or invisible background processes. Using the five category tabs at the top of the Activity Monitor window, you can see how each category of processes is impacting your Mac.
CPU
The CPU tab displays how processes affect CPU (processor) activity. Click on the "%CPU" column header to sort by the percentage of CPU capability each process uses.
Memory
The Memory tab provides information on memory usage. As long as memory pressure is not in red, macOS has available memory resources.
Energy
The Energy tab shows overall energy consumption and the energy usage of each application. As energy consumption increases, the battery life of your Mac may decrease.
Disk
The Disk tab displays the amount of data each process has read from and written to the disk. It also shows "reads" and "writes" (IO), which are the number of times your Mac accesses the disk to read and write data.
Network
The Network tab shows the amount of data your Mac is sending or receiving over the network. Use this information to determine which processes are sending or receiving the most data.
Cache
The Cache tab displays how much cache content local network devices have uploaded, downloaded, or purged over time. Use the "Maximum Cache Pressure" information to understand whether to adjust cache settings to provide more disk space for caching. Lower cache pressure is better.
Forcing Quit Applications with Activity Monitor
When a website or running application freezes on your Mac, and you seem stuck with nowhere to go, knowing how to force quit becomes essential. Similar to Windows' Control + Alt + Delete, Mac also has this magic shortcut accessed by Command + Option + Escape to bring up the Force Quit window.
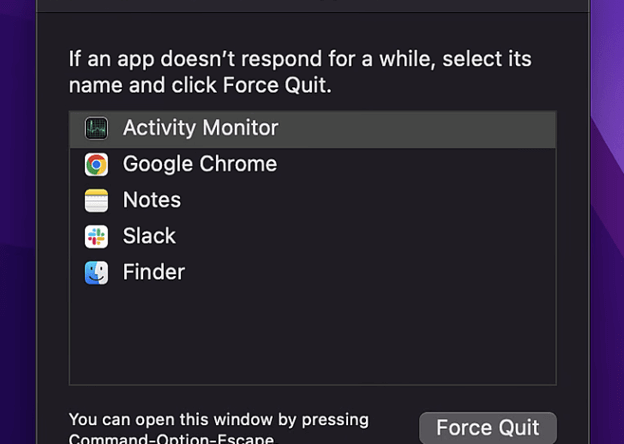
Alternatively, you can use Activity Monitor to force quit applications by following these steps:
1. Open Activity Monitor: Launch Activity Monitor using the methods described earlier.
2. Identify the Application: In the Activity Monitor window, locate the application you want to force quit. You can use the search bar or sort the processes by name or resource usage to find the application.
3. Select the Application: Click on the application to select it.
4. Force Quit: With the application selected, click the "X" button in the toolbar or choose "Force Quit" from the "View" or "Process" menu.
5. Confirm: A dialog box will appear asking if you want to force quit the application. Confirm by clicking "Force Quit."
6. Monitor System Behavior: After force quitting the application, monitor your system's behavior to see if the issue has been resolved. If necessary, troubleshoot further or restart your Mac if the problem persists.
How to Recover Deleted Data on Mac
If you've encountered the issue of deleted data on your Mac and are worried about potential data loss, consider using a specialized data recovery program like AnyRecover Data Recovery for Mac. This technical software is designed to help Mac users recover lost or deleted files caused by file system errors, system failures, or unintentional deletions. Additionally, you can utilize this software to recover deleted files that have been emptied from the Trash on your Mac (including MacBook Pro and other models).

Features of iMyFone AnyRecover:
- All-inclusive data recovery: AnyRecover is capable of recovering 1000+ file formats.
- 100% safe data recovery: You can use this tool to recover your deleted files without worrying about overwriting your existing data.
- No any backups requirement: AnyRecover directly scans the drive location you specify in order to find your deleted data.
- User-friendly interface and easy-to-use, powerful data recovery operations.
- Fully compatible with Mac OS X 10.9 to Mac OS X 10.15 and others.
Steps to Recover Deleted Files on Mac Via AnyRecover:
Step 1. Open AnyRecover on your Mac and navigate to the location where your files were stored before deletion. Click on the Start button to initiate the process.
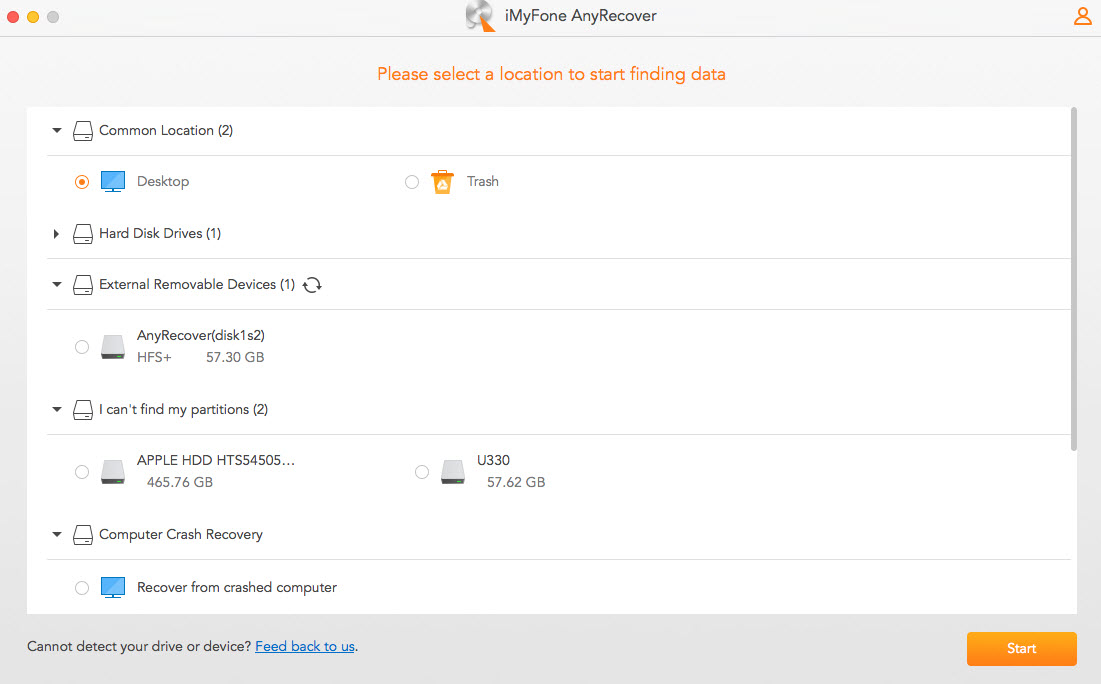
Step 2. AnyRecover will commence the comprehensive scanning process to locate all deleted files on your selected location. Please wait until the scan is finished.
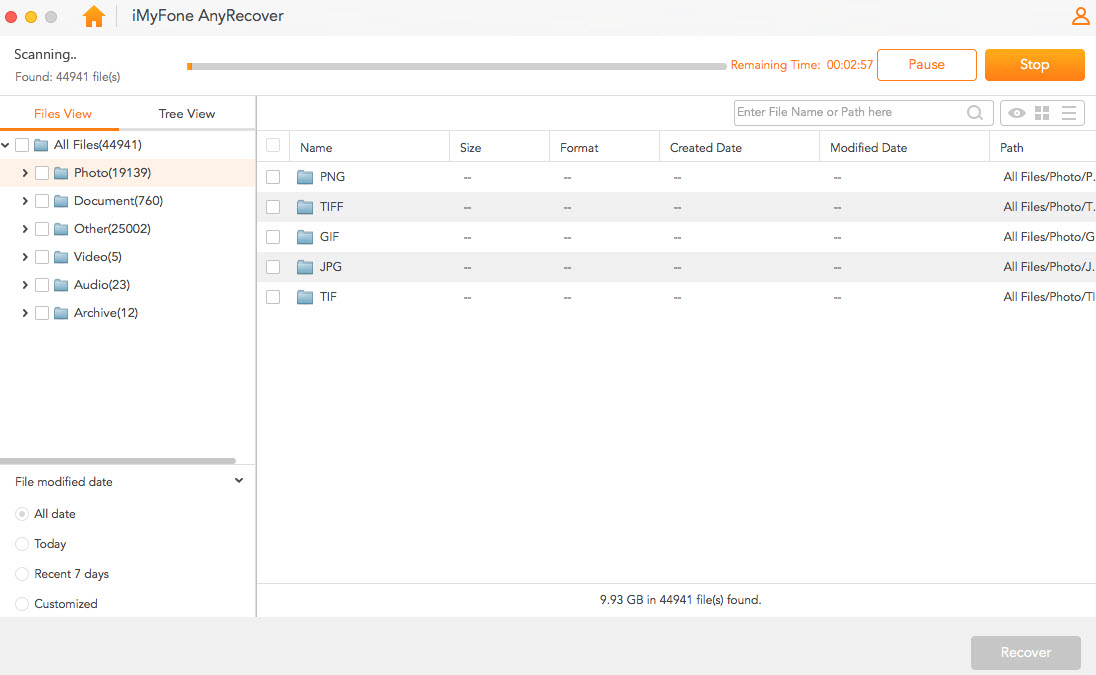
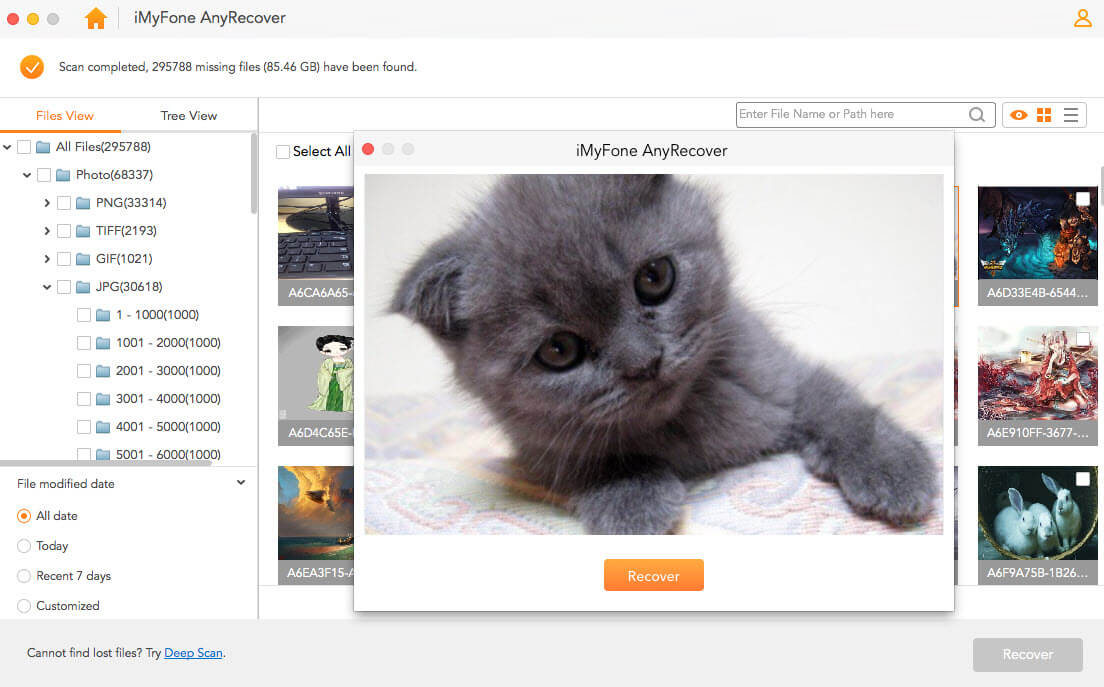
Step 3. After the scan completes, you'll see the list of recoverable files on the left side. Select the files you wish to recover, then click on the Recover button to start the data recovery process.
The Final Words
Mastering the Task Manager, or Activity Monitor, is crucial for effectively managing your Mac's performance. By following the methods outlined in this guide, you'll be able to open and utilize Task Manager with ease, ensuring smooth operation of your Mac.
AnyRecover can help you recover all kinds of data on your Mac quickly and efficiently. Try it for free and recover your data from Mac now!
FAQs about How to Open Task Manager on Mac?
Can I customize Task Manager settings on Mac?
Yes, you can customize Task Manager settings on Mac to suit your preferences. From the Activity Monitor menu, select "View" and then "Dock Icon." Here, you can choose to display CPU usage, memory usage, disk activity, or network activity in the Dock icon, providing quick access to vital system information.
Are there any third-party Task Manager alternatives for Mac?
Yes, several third-party Task Manager alternatives are available for Mac, offering additional features and functionalities. Some popular options include iStat Menus, CleanMyMac X, and App Cleaner & Uninstaller. These tools provide comprehensive system monitoring and optimization capabilities, enhancing your Mac experience.
What should I do if Task Manager is not responding on Mac?
If Task Manager is not responding on Mac, you can force quit the application using the "Force Quit" option from the Apple menu or by pressing Command + Option + Escape. Alternatively, you can use Terminal to terminate the Activity Monitor process manually. If the issue persists, consider restarting your Mac to resolve any underlying software conflicts.
How can I monitor system performance using Task Manager on Mac?
Task Manager on Mac provides detailed information about CPU usage, memory usage, disk activity, and network activity, allowing you to monitor system performance effectively. Simply open the Activity Monitor and navigate to the relevant tabs to view real-time statistics and identify any potential bottlenecks or issues affecting your Mac's performance.
Related Articles:
- Troubleshooting Guide: How to Fix Mac Desktop Files Disappeared
- Mac Trash Guide: Can I Recover Deleted Files in Recycle Bin Macbook
- [2024] How to Fix “The Recovery Server Could Not Be Contacted”
- 4 Effective Ways to Recover Files from External Hard Drive on Mac
- [Fixed] How to Detele Photos from Mac? 4 Ways!
- Troubleshooting Guide: How to Fix Desktop Files Disappeared Mac
Time Limited Offer
for All Products
Not valid with other discount *

 Hard Drive Recovery
Hard Drive Recovery
 Deleted Files Recovery
Deleted Files Recovery