How to Recover Data from RAID Disk in 2024?
Data loss from RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) systems can be a daunting experience for individuals and organizations alike. Whether it's due to hardware failures, human error, or other unforeseen circumstances, the loss of critical data can have significant consequences.
However, with the right knowledge and tools, it's possible to recover data from RAID arrays and minimize the impact of such incidents. In this article, we'll explore the steps and strategies for effectively recovering data from RAID configurations. Let's get started!

Part 1: What is RAID Configurations?
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. It's a technology used to combine multiple physical disk drives into a single logical unit for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both. There are several RAID configurations, each offering different levels of redundancy, performance, and capacity. Here are some common RAID levels:

These are just a few examples, and there are other RAID configurations as well, each with its own advantages and trade-offs. The choice of RAID configuration depends on factors such as performance requirements, redundancy needs, and budget constraints.
Part 2: Common Causes of Data Loss in RAID Systems
While RAID systems are designed to provide data redundancy and fault tolerance, they are not immune to data loss. Several factors can lead to data loss in RAID systems:
To mitigate the risk of data loss in RAID systems, it's important to regularly back up data, maintain hardware and software components, implement proper security measures, and follow best practices for RAID configuration and management. Additionally, having a thorough understanding of the chosen RAID level and its limitations can help in making informed decisions to safeguard data.
Part 3: How to Recover Data from RAID Disk?
If you're facing data loss issues with your RAID array and want to recover data from RAID set, AnyRecover could be the solution you need. It's a powerful tool designed to recover lost or deleted files from various storage devices, including RAID arrays.

1,000,000 + Downloads
Features of AnyRecover
- AnyRecover makes RAID set recovery simple and straightforward, with an intuitive interface that guides you through the process.
- AnyRecover can handle a wide range of data loss scenarios, including drives becoming raw or formatted, partitions getting lost, accidental deletion, and more.
- It supports data recovery from a variety of storage devices and partitions, including USB drives, SD cards, hard drives, flash drives, and RAID arrays.
- It supports almost all widely used file systems, such as NTFS, FAT, FAT32, and more.
- AnyRecover is available for both Windows and Mac OS, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
Steps to recover data from RAID with AnyRecover
Step 1. Download and launch AnyRecover, and click on "PC & Hard Drive Recovery" on the homepage.
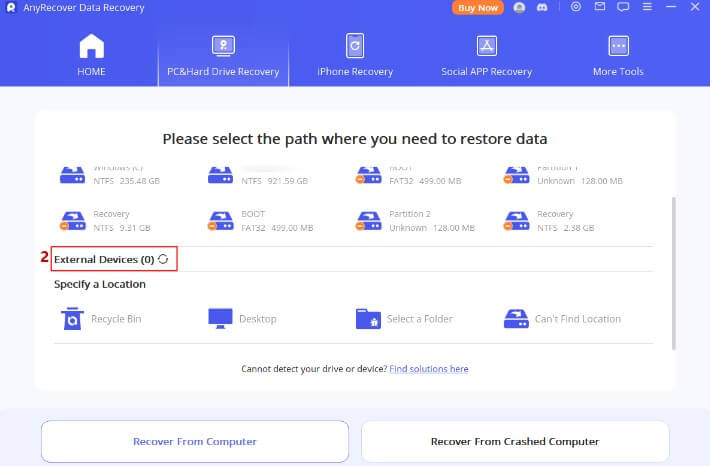
Step 2. Then, connect your RAID array to your computer, and you will find it be detected under External Devices. Click it to scan the files in your RAID.
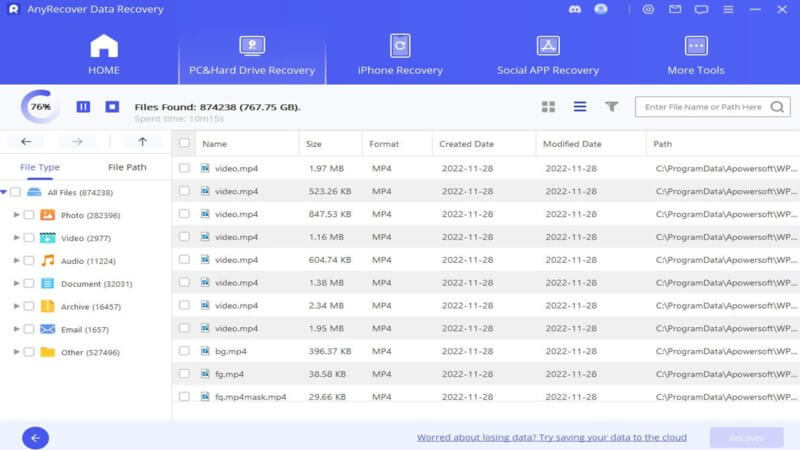
Step 3. After the deep scanning, select the files you want to restore, and click "Recover" to get it back.
Part 4: FAQs about RAID Data Recovery
Can you recover data from a RAID drive?
Yes, data recovery from a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) drive is possible, but it can be more complex than recovering data from a single drive. Using data recovery tool like AnyRecover can help to recover data from RAID.
How much does it cost to recover data from RAID?
Data recovery from common RAID configurations typically costs between $300 to $1,900. The price depends on factors like the severity and type of failure, complexity of recovery, and the number of hard drives in the RAID. Using software for RAID data recovery -- AnyRecover can be cost-effective compared to professional services.
Is A RAID better than a backup?
No, RAID is not better than a backup. RAID provides redundancy and fault tolerance within a storage system, while backup creates separate copies of data for protection against various data loss scenarios. Both serve different purposes and are essential components of a comprehensive data protection strategy.
Conclusion
After viewing the above method, I believe that you can recover data from RAID with ease and without much cost. But still, please remember that prevention is the key, so make sure to implement robust backup strategies and proactive maintenance to safeguard against future data loss.
AnyRecover
10% Discount Coupon Code: RECOVER9
Time Limited Offer
for All Products
Not valid with other discount *

 Hard Drive Recovery
Hard Drive Recovery
 Deleted Files Recovery
Deleted Files Recovery
